医疗旅游首选地:马来西亚 MR
你知道吗?越来越多来自世界各地的患者选择.
Diagnostic imaging comprises various techniques to view the inside of the body. This allows doctors to find indications of a health condition, diagnose the condition, or to see how well a patient is responding to treatment.
Imaging tests include X-Ray, Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI and PET scans are mostly non or minimally invasive. Read on to find out what they are, the differences, and what they are generally used for.
目录
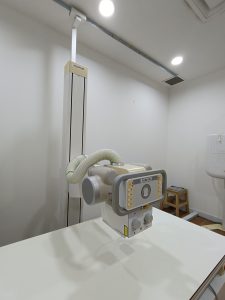
ToggleX-ray machines emit electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of tissues, bones, and organs Standard X-rays may be used for a variety of reasons, including diagnosing tumours or injuries to bones. X-ray scans expose patients to radiation.
X-rays are also used in technology is used in other types of diagnostic imaging, such as CT scans.
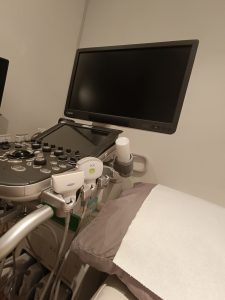
Another diagnostic imaging technology is ultrasound. This non-invasive imaging test uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures or videos of internal organs or other soft tissues in real-time. Ultrasound does not involve the use of radiation. Ultrasound can help the doctor investigate a variety of conditions, such as unexplained pains, lumps, or the causes of abnormal blood tests.
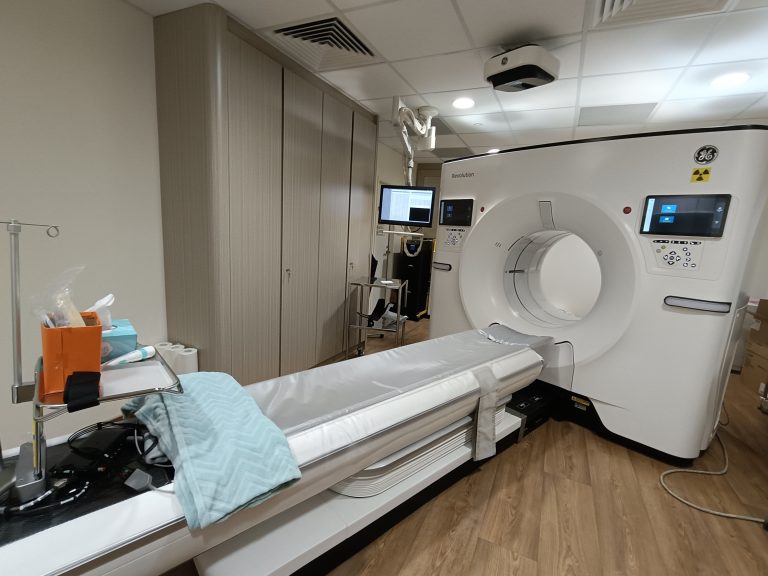
CT (computed tomography) scans use X-rays to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. They are often used to diagnose cancer, heart disease, injuries from trauma, and musculoskeletal disorders. Like standard X-Rays, radiation is used in CT scans.
• Multiple cross-sectional images of the body are taken and re-assembled in a computer to show the internal organs and other structures (e.g. bones, blood vessels).
• Can be rotated to allow the radiologist to view it from various angles.
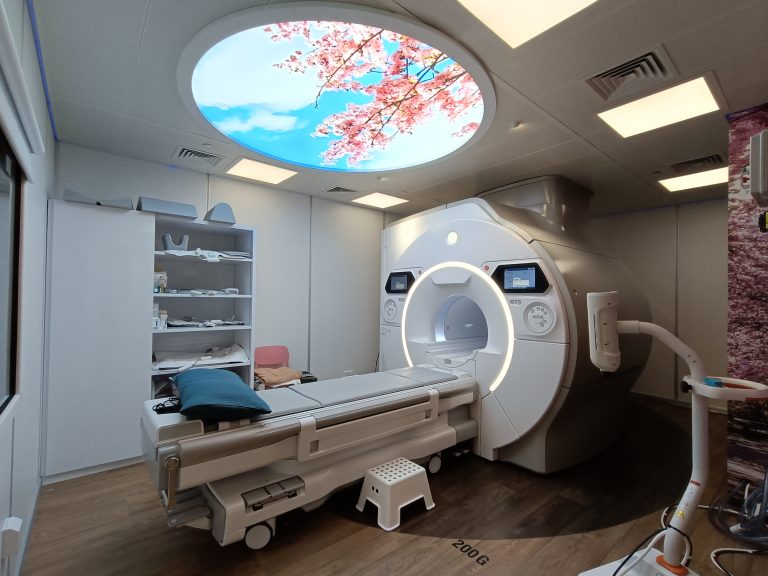
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) creates detailed images of organs and other structures inside the body using a powerful magnet and radio waves. Patients undergoing this test must remove metal items and inform the technician of any internal devices (e.g. pacemaker) that contain metal. MRI is used to diagnose conditions including ligament injuries and tumours.
• MRI scans may require a contrast agent that is injected through an IV line to allow a better view of the area under study.
• Like CT scan, MRI shows the structure of the body, but produces different set of information.
• Takes longer to perform than a CT and is more expensive.
• Does not expose patients to radiation.
A PET (positron emission tomography) scan is used to visualise the metabolism or chemical activity within the body. Unlike CT and MRI scans that look at the form of structures inside the body, a PET scan looks at the functioning of the body and detected unusual cellular activity. A PET scan may be used to diagnose cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders such as dementia or Alzheimer’s.
PET scans may often be combined with a CT scan for a more complete picture (PET / CT Scan).
X-Ray | Ultrasound | CT Scan | MRI | PET Scan | |
What Does It Show? | Structure of tissues / organs / bones. | Structure of tissues / organs / bones. | Structure of tissues / organs / bones. | Structure of tissues / organs / bones. | Metabolism or chemical activity in the body. |
What Are The Common Diagnostic Uses? | Tumours or injuries to bones. | Unexplained pains, lumps, or the causes of abnormal blood tests. | Cancer, heart disease, injuries from trauma, and musculoskeletal disorders. | Ligament injuries, brain disorders, and tumours. | Cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders. |
Radiation Exposure? | Yes. | No. Uses sound waves. | Yes. | No. Uses magnet and radio waves | Yes (from radiotracers). |
The actual cost of diagnostic imaging will depend on the choice of hospital / imaging centre, and also on the specifics of the scan required. Some general costings are tabulated below as a guide for easy reference. Certain scans such as PET scans that require special radiotracers may cost substantially more.
Singapore | Malaysia | |
X-Ray | S$50 - 100 | RM 50 - 200 |
Ultrasound | S$130 - 200 | RM 100 - 200 |
CT Scan | S$400 – 1,400 | RM 3000 – 3300 (PET / CT Scan) |
MRI | S$1,000 – 2,000 | RM 1,000 |
PET Scan | S$2,500 – 4,000 | RM 3000 – 3300 (PET / CT Scan) |
Health365 has healthcare partners in Singapore and Malaysia that provide diagnostic imaging services. Contact us to enquire.
Related Articles You Might Be Interested In
